China Medical Visas
China medical visas are official immigration permits required for foreign nationals seeking medical treatment in mainland China. The Chinese government categorizes these healthcare-specific visas into distinct types: S1 visas for long-term treatments exceeding 180 days, S2 visas for short-term medical stays up to 180 days, and limited L visa usage for minor consultations under 30 days. Selecting the incorrect visa category results in application rejections, entry denials at immigration checkpoints, and treatment delays.
Understanding China medical visas requirements is essential for anyone intending to embark on China for medical treatment, rehab program use, or specialist health treatments in a Chinese hospital. This guide has everything you will need to obtain china medical visas for your healthcare journey. You’ll find all of the S2 visa types of medical situations, whether you can apply, and the step by step S2 visa process from hospital documents to when you collect your embassy visa.
⭐ Choosing Your China Medical Visa: S1, S2, and L Options
Medical Visa Categories Explained: S1, S2, and L Visa Comparison
| Feature | S1 Visa | S2 Visa | L Visa (Limited) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stay Duration | >180 days, convert to residence permit (up to 5 years) | ≤180 days | <30 days |
| Accompanying Family | Spouse, parents, children under 18 | Spouse, parents, children, grandparents, siblings | None specified |
| Core Documents | Long-term treatment certificate + financial proof (120% costs) | Short-term diagnosis + bank statement (>$10,000 USD) | Hotel booking only |
| Ideal For | Cancer, transplants, complex surgeries | Short surgeries, rehabilitation, checkups | Simple consultations only |
| Hospital Requirements | Grade A Level 3 hospital letter | Grade A Level 3 hospital letter | Not required |
China medical visas fall into three main categories for healthcare travelers. Each type serves different treatment durations and purposes. Selecting the correct visa prevents delays and rejections.
S2 Visa serves as the primary china medical visas option for most patients. This visa covers short-term treatments lasting up to 180 days. Patients can obtain single, double, or multiple-entry options. Authorities permit two 90-day extensions within China.
S1 Visa applies to long-term medical treatments exceeding 180 days. Cancer treatments, organ transplants, and complex surgeries qualify. Holders must convert to residence permits within 30 days. These permits can remain valid for up to five years.
L Tourist Visa Limitations: L visas only permit minor medical consultations. Hospitals refuse inpatient procedures for L visa holders. Border officials may deny entry when discovering medical intent. Always apply for S2 visa for planned treatments.
Non-Qualifying Medical Purpose: M, Z, Q2 and Medical Testing
M-Visa is for Commercial and Trade Visa, NOT Medical Visa. This misconception gets thousands of china medical visas rejected every year. The M-Visa is tailored by the Chinese government for business purposes. Business Travellers will apply this category visa to attend exhibitions like Canton Fair. Visiting factories and meeting for contract negotiations also qualify. But Do Not Apply M-Visa for getting medical treatment. This plainly constitutes a visa misuse under Chinese law.
Z Visa serves work purposes, not medical treatment. Foreign employees need Z visas for employment in China. Never confuse Z visa with china medical visas options. Q2 Visa applies when visiting Chinese citizens or permanent residents. The patient receiving care must hold Chinese citizenship. Eligible relationships include spouse, parents, children, and siblings. This differs significantly from S2 medical purposes.
Medical Testing Differs from Medical Visas. Health examinations verify applicant fitness. China medical visas require hospital invitations. Testing confirms absence of diseases. Both serve different immigration purposes.
⭐ Medical Applicant Eligibility Criteria: Who Qualifies, Who Doesn't, and Alternative Solutions

Applicants for Medical Visas
Medical Eligible Applicants: Requirements and Typical Medical Travel Scenarios
Qualified applicants possess official hospital invitations from Grade A Level 3 institutions. Financial capability proves essential for china medical visas approval. Passports must maintain six months validity with blank pages.
Basic Qualification Requirements:
- Official diagnosis or invitation from Chinese Grade A Level 3 hospital
- Financial proof covering 120% of estimated medical costs (minimum $10,000 USD recommended)
- Passport valid for six months beyond intended stay
- At least two blank visa pages available
- No active infectious disease history
Cancer patients seeking advanced treatments in China qualify readily. Organ transplant candidates and complex surgery patients receive priority consideration. Chronic disease management and rehabilitation programs also qualify. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) treatment seekers can obtain china medical visas.
How to Obtain Medical Certificates from Chinese Hospitals
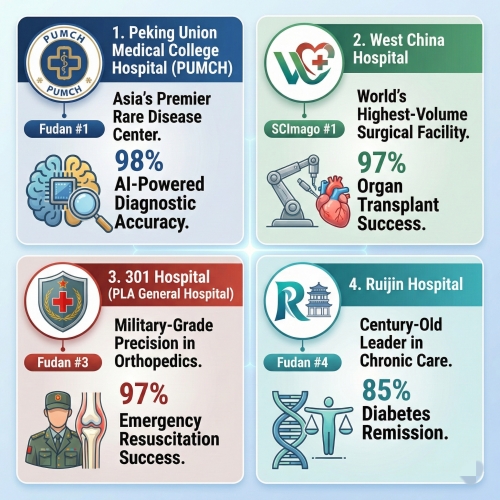
A critical component of your china medical visas application is the medical certificate. Only Grade A Level 3 hospitals or designated institutions in China can issue valid certificates. Examples include Ruijin Hospital in Shanghai and Peking Union Medical College Hospital in Beijing. These certificates must be in Chinese or accompanied by official translation and stamped with the hospital's seal.
Specific Access Channels:
Ineligible Applicants: Medical and Administrative Disqualifications
Active infectious diseases trigger automatic china medical visas rejections. Untreated tuberculosis, syphilis complications, and certain conditions disqualify applicants. Though China removed HIV entry bans in 2020, uncontrolled cases may face scrutiny.
Severe mental illnesses threatening public safety cause disqualifications. Criminal records and blacklisted nationalities prevent visa issuance. Afghanistan and Iran nationals face additional restrictions. Insufficient passport validity or missing documents guarantee rejections.
Common rejection reasons include: incomplete hospital invitation letters, insufficient financial documentation, failed medical examinations, and providing false information. Format errors in hospital documents cause frequent problems. Embassies cross-check hospital credentials against government databases continuously. Invalid documents trigger automatic rejections without appeal.
Alternative Solutions: Options for Ineligible or High-Risk Applicants
Ineligible applicants can explore visa-free entry options. Fifty-five countries enjoy 30-day exemptions for simple treatments. The 240-hour transit program serves quick consultations during layovers. Hainan Province offers specialized medical tourism access.
L tourist visas work for treatments under 30 days. Remote consultations can establish treatment plans before travel. Medical tourism agencies assist with documentation procurement. Patients then convert to proper S2 visas with complete paperwork.
Hong Kong and Macau operate independent visa systems. Patients can transit through these regions for Chinese medical access. Specialized agencies provide comprehensive support for complex cases. HIV or syphilis patients should complete treatment first. Negative test results strengthen subsequent visa applications significantly.
⭐ S2 Visa Application Guide: Complete Step-by-Step Process
Step 1 - Hospital Documentation: Obtaining Official Medical Invitation from Qualified Institutions
Medical Invitation Letters are used by China visa applicants for medical purposes. You’ll need to seek invitations from Grade A Level 3 public hospitals or approved international clinics only. And hospital credentials must be stamped with the official seal for the invitation letters as well.
You’ll need to provide the patients’ full names and passport numbers in the invitation letters. Diagnosis summary and issue should be evident, as well as treatment plans and hospitalization dates (especially when staying overnight). In addition, see hospital contact details and name and signature of authorizing hospital personnel. And also be sure the estimated treatment costs arestated in the letter.
Documents must appear in Chinese or English languages exclusively. Other languages require certified translation with translator official seals. Embassies verify hospital credentials against government databases continuously. Invalid documents trigger automatic application rejections without appeal options.
Step 2 - Online Application: Completing COVA System with Precision
The China Online Visa Application system operates at https://consular.mfa.gov.cn/VISA/. Applicants must select "S2" visa type carefully. Specify "medical treatment" as the exact purpose clearly.
Duration requests should match treatment timelines precisely through available options. Thirty, sixty, ninety, and 180-day stays accommodate different procedures. Photo specifications require 35mm×45mm dimensions with white backgrounds exclusively. Blurry passport scans below 300 DPI resolution cause system rejections.
Step 3 - Document Assembly: Comprehensive Checklist for Embassy Submission
Passport originals must maintain minimum six months validity from entry. At least two blank visa pages accommodate stickers and stamps. Recent passport photos measuring 35mm×45mm need two copies with white backgrounds.
Required Document Package:
- Passport original (6+ months validity, 2 blank pages)
- Hospital invitation letter original + diagnosis certificate
- Financial proof (bank statements ≥ $5,000 USD, recommend $10,000+)
- Round-trip flight reservations (purchase not required)
- Accommodation confirmation (hotel booking or invitation address)
- Travel insurance certificate (recommended $50,000+ medical coverage)
- Two passport photos (35mm×45mm, white background)
- Certified translations for non-English/Chinese documents
- Previous medical records (English or Chinese bilingual versions)
- Employment letter (if maintaining job during treatment)
Medical documents include hospital invitation originals and diagnosis certificates. Previous medical records require English or Chinese bilingual versions. Financial proof demonstrates minimum $5,000 USD equivalent balance. Travel insurance covering medical emergencies complements application packages.
Step 4 - Embassy Submission: In-Person, Mail, or Agency Application Methods
Submission options include in-person visits to embassy or consulate locations. Mail-in submissions work for US and Australian applicants specifically. Authorized agency services suit travelers with limited time availability.
Appointment requirements exist at most embassies needing 7-10 day advance booking. Peak seasons increase waiting periods during summer and holidays. Applications should occur minimum 15 business days before departure. Submit applications 4-6 weeks before treatment appointments ideally.
Step 5 - Status Tracking: Monitoring Your Application Progress
Tracking methods include COVA system online checks using application numbers. Embassy websites provide query functions with updated processing statuses. SMS notification enrollment provides real-time updates on applications.
Processing timelines follow standard service at 4-5 business days typically. Expedited service reduces processing to 2-3 business days with fees. Rush service provides 1 business day turnaround for emergencies. Not all embassies offer fast-track options available.
| Processing Type | Timeline | Additional Fee | Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | 4-5 business days | None | Complete documentation |
| Expedited | 2-3 business days | $30-50 USD | Urgent travel proof |
| Rush (Emergency) | 1 business day | $100+ USD | Critical illness documentation |
Step 6 - Visa Collection: Retrieval Options and Verification Checklist
Collection options permit in-person pickup with receipts and identification. Authorized representatives require notarized authorization letters for proxy collection. Courier delivery services operate with prepaid envelope provisions.
Verification checklist demands immediate name spelling and validity date checks. Entry number confirmation ensures proper authorization. Permitted stay duration requires verification against requested timelines. Error correction must occur within 24 hours before departures.
Medical Examination Requirements: Pre-Visa Health Screening Details

Medical Treatment for Foreigners in China
Before submitting your china medical visas application, you may need to complete a medical examination. This section explains when examinations are required, what tests are included, and how to handle the results.
Examination Triggers: Who Needs Medical Testing
S2 visas less than 180 days exemption from medical examination. Certain categories of medical tourists are also potentially exempt from the medical examination requirement. Management restrictions, and exemptions, below such as for a stay of less than 6 months.
If traveling from specific countries or region with an endemic epidemic you may be asked to undergo screening, currently around 25% of S2 applicants are required to undergo a health screening before entry, just prior to Covid policy changes were made following the global pandemic in 2023. China completely lifted mandatory health checks for the majority of short stay categories.
Required Medical Tests: Comprehensive Health Screening Components
Physical examination assesses blood pressure, pulse rate, and respiratory rate. General physical condition evaluation completes basic health screening. Electrocardiogram testing checks cardiovascular function for all exam-required applicants.
Chest X-ray examination remains mandatory for tuberculosis screening universally. Blood tests panel includes HIV antibody screening and syphilis tests. Liver function markers ALT and AST plus Hepatitis B complete testing. Urinalysis screens kidney function and diabetes presence through samples.
| Test Category | Specific Tests | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Exam | Blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate | General health assessment |
| Chest X-Ray | Lung imaging | Tuberculosis screening |
| Blood Tests | HIV, syphilis, liver function (ALT/AST), Hepatitis B | Infectious disease detection |
| Urinalysis | Kidney function, glucose levels | Diabetes and kidney screening |
| ECG | Heart rhythm analysis | Cardiovascular function |
Complete screening takes 2-3 hours at approved clinic locations. Results validity extends six months from issue date. Format requirement mandates using official "Foreigner Physical Examination Form" exclusively. China immigration authorities reject unofficial or improperly formatted reports.
Approved Examination Facilities: Embassy-Designated Clinics by Country
United States approved providers include IOM designated clinics in major cities. New York, Los Angeles, San Francisco, Chicago, and Houston offer services. Cost range spans $150-$300 USD depending on locations.
| Country | Approved Providers | Major Cities | Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | IOM Designated Clinics | NYC, LA, SF, Chicago, Houston | $150-$300 USD |
| United Kingdom | Panel Physician Clinics | London (Harley Street, The Doctors Laboratory) | £450-£539 GBP |
| Australia | Bupa Medical Visa Services | Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth | AUD 350-$450 |
United Kingdom designated providers operate as Panel Physician clinics. London clinics include Harley Street Medical Centre locations. Australia approved network operates through Bupa Medical Visa Services. Appointment scheduling needs 1-2 weeks advance notice typically. Results timeline provides sealed medical reports within 3-5 business days.
Failed Examination Management: Handling Adverse Results and Appeal Options
Automatic disqualifications include active tuberculosis without treatment completion. Untreated communicable diseases posing public health risks cause rejections. Severe mental illness with safety concerns disqualifies applicants.
HIV policy clarification: China removed HIV entry ban in 2020. HIV-positive individuals obtain visas with viral load control documentation. Common failure reasons include abnormal chest X-rays from previous TB. Elevated liver enzymes and positive syphilis serology trigger reviews.
Consult immigration attorneys for case-specific guidance when health issues exist. Medical waivers occasionally grant exceptions based on individual circumstances. China medical visas authorities consider humanitarian factors in complex situations. Failed examinations do not automatically mean complete visa denial.
Visa Fees and Processing Timeline: Budgeting for Your Application
Once you've completed any required medical examinations, understanding the costs and timeline helps you plan your china medical visas application effectively.
Base Visa Fees: Country-Specific Pricing Structure for 2026
China medical visas costs vary significantly by applicant nationality. United States citizens pay $140 standard fee through December 2025. This unified fee covers single, double, and multiple-entry applications. Direct embassy applications eliminate additional service charges for Americans.
| Country | Single Entry | Double Entry | Multiple Entry | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $140 USD | $140 USD | $140 USD | Unified fee structure |
| United Kingdom | £130 | £170 | £191-255 | Through CVASC |
| Australia | AUD 94.50 | AUD 117.50 | Varies | CVASC locations |
| Canada | CAD 137.15 | CAD 137.15 | CAD 137.15 | Fixed fee structure |
| Germany/France | EUR 110.45 | EUR 110.45 | EUR 110.45 | Through CVASC |
| Japan | Visa-free until Dec 31, 2026 | 30-day exemption |
United Kingdom applicants face £130 standard fee through China Visa Application Centers. Five-year multiple-entry visas cost £170 while 10-year options reach £191-255. Australian citizens pay AUD 94.50 for single-entry applications. Canadian applicants encounter CAD 137.15 fixed fees regardless of entry numbers.
Additional Cost Components: Beyond the Base Visa Fee
Additional VFS Global fee ($30-$50 USD) if using a visa service center, possible photo services ($10-$20 USD) if you need someone to take your photo, document translation fees ($30-$80 USD per page) if you need your medical reports & documents converted. Medical examinations ($150-$400 USD) if you’re going for more long-term stays greater than 6 months. Insurance costs ($50-$200 USD if you want a higher premium).
The passport courier/postage mailing charge ($15-$30 USD). This can end up costing US applicants somewhere between $350-$700 USD or so.
Processing Time Variables: Standard Timeline and Peak Season Delays
Standard timeline breakdown includes hospital documents requiring 3-7 days. Document preparation consumes 2-3 days for gathering and translation. Embassy processing adds 4-5 days creating 2-3 week totals.
| Phase | Duration | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital Document | 3-7 business days | Contact hospital international department |
| Document Preparation | 2-3 days | Gather, translate, organize materials |
| Embassy Processing | 4-5 business days | Submit and wait |
| Total Timeline | 2-3 weeks | Complete process |
Peak season delays occur during Chinese New Year from January-February periods. Summer vacation months of July-August add 3-5 business days. National Day holiday in October similarly impacts speeds. High-demand embassies like New York require booking 10-14 days ahead.
Visa-Free Entry Options: Alternatives to Traditional China Medical Visas

Beijing Daxing International Airport
If the standard visa application process seems daunting, or if you only need short-term medical services, visa-free entry options may work for you. These alternatives to traditional china medical visas can simplify your journey significantly.
55 Countries 30-Day Exemption: Simplified Access for Routine Medical Services
China extended unilateral visa exemption to 55 countries through December 2026. The National Immigration Administration implemented this policy for tourism and medical purposes. Thirty-day visa-free entry eliminates application requirements for qualifying nationals.
Eligible Countries for China’s 240-hour Visa-Free Transit (as of June 2025)
| Continent | Countries |
|---|---|
| Europe | Austria, Belgium, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Norway |
| Asia | Japan, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, Brunei, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Israel, Indonesia (added in 2025) |
| Americas | United States, Canada, Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand |
| Other Europe (non-Schengen) | United Kingdom, Ireland, Croatia, Serbia, Ukraine |
| Total | 55 countries |
Patients simply present passports at immigration without advance applications. Extension beyond 30 days remains impossible under visa-free rules. Conversion to other visa types equally proves unavailable after entry. Ideal scenarios include annual health checkups and dental tourism.
240-Hour Transit Visa-Free: Medical Opportunities During Extended Layovers
The 10-day transit exemption applies to 55 nationalities passing through China. Travelers need confirmed onward tickets to third countries or regions. Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan count as third destinations.
Eligible entry points include Beijing Capital and Daxing international airports. Shanghai offers access through Pudong Airport, Hongqiao Airport, and cruise ports. Guangdong permits entry via Guangzhou Baiyun Airport and Shenzhen. Geographic restrictions limit travel within designated provinces only.
Hainan Boao Lecheng Zone: Specialized Medical Tourism Hub with Enhanced Access
Hainan Boao Lecheng International Medical Tourism Pilot Zone provides advantages. Fifty-nine countries enjoy 30-day visa-free entry specifically for Hainan. The policy explicitly permits medical treatment as entry purpose.
Access to drugs and medical devices unavailable elsewhere distinguishes Boao. Over 525 specially approved medications exceed mainland China's standard offerings. FDA-approved medications arrive within three months for patient use. Advanced treatments include stem cell therapy and proton radiotherapy.
| Feature | Advantage | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Visa Access | 59 countries, 30-day free | Specifically for Hainan medical tourism |
| Medications | 525+ approved drugs | FDA-approved, unavailable in mainland |
| Treatments | Advanced therapies | Stem cell, CAR-T, proton therapy |
| Cost | 30-60% lower | Compared to Singapore/Hong Kong |
| Patient Volume | 150,000 in 2024 | 15% annual growth |
CAR-T immunotherapy and latest cancer medications attract international patients. Popular specialties encompass oncology treatment, aesthetic medicine, and anti-aging. Patient volume reached 150,000 international visitors in 2024. Treatment costs run 30-60% lower than Singapore prices. Over 30 medical institutions operate with 27 international clinics.
Post-Arrival Compliance: What to Do After Landing in China
After successfully obtaining your china medical visas and arriving in China, your responsibilities don't end. Understanding post-arrival requirements ensures you maintain legal status throughout your medical treatment.
30-Day Residence Registration: Legal Obligation and Compliance Process
All foreign nationals must register temporary residence within 30 days. This requirement stems from PRC Exit and Entry Law Article 39. Hotel accommodation triggers automatic electronic registration with receipt provision.
Private residence situations require landlord accompaniment to local police stations. Required documents include passport originals and visa page photocopies. Accommodation proof through lease contracts or property deeds becomes necessary. Registration process involves taking queue numbers at counters.
S2 Visa Extension: Requirements and Application Procedure
Extension eligibility permits maximum two extensions with 90-day limits each. Application timing demands submission minimum seven days before expiry. Processing location centers on Public Security Bureau Exit-Entry Administration.
Required documents include passport originals and visa extension application forms. Temporary residence registration and hospital continuation treatment certificates prove necessary. Accommodation proof and passport photos complete standard requirements. Extension fees cost ¥160 RMB per extension approximately.
Residence Permit Conversion: Long-Term Treatment Beyond 180 Days
Conversion eligibility serves medical treatments requiring stays beyond 180 days. Cancer chemotherapy, rehabilitation therapy, and chronic disease management qualify. Application windows require valid S2 visa periods without expired status.
Residence permit durations receive typical 6-month to 1-year issuances. Annual renewals extend permits based on ongoing treatment necessity. Additional requirements include completing "Foreigner Physical Examination Record" at hospitals. Detailed treatment plans and cost payment proof demonstrate capability.
| Permit Duration | Fee (RMB) | Requirements | Renewal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 Months | ¥400 RMB | Health check within 30 days | Apply before expiry |
| 1 Year | ¥800 RMB | Health check + treatment plan | Annual review |
Frequently Asked Questions About Chinese Medical Visas
Q: How to get a Chinese medical visa?
Obtain hospital invitation from Grade A Level 3 Chinese institution. Complete COVA online application selecting S2 visa type. Gather required documents including passport, financial proof, and photos. Submit application at Chinese embassy with all materials. Track status online and collect approved visa. The complete process requires 2-3 weeks typically. Start applications 4-6 weeks before treatment dates.
Q: Can a visa be rejected due to medical reasons?
Yes, active infectious diseases cause immediate rejections definitely. Untreated tuberculosis and uncontrolled HIV may trigger denials. Positive syphilis results require treatment completion certificates. Severe mental illnesses threatening safety disqualify applicants. Failed medical examinations from approved clinics lead to refusals. However, China removed HIV entry ban in 2020. Controlled viral loads with documentation allow approval. Appeal options exist with specialist opinion letters.
Q: Can Americans go to China for healthcare?
Yes, Americans can access Chinese healthcare through S2 visas. US citizens pay $140 unified fee for applications. Provide hospital invitation, financial statements, and medical records. Many American patients travel to Shanghai and Beijing. Success rates exceed 95% with complete documentation. Case example: American cardiac patient received S2 approval. His application processed within seven days successfully. China welcomes American medical tourists actively.
Q: Can I use L tourist visa for medical treatment?
Technically possible to enter on L visa but risky. Immigration officers may deny entry discovering medical intent. Hospital international departments refuse L visa inpatient procedures. Regulatory compliance issues prevent accepting inappropriate categories. Travel insurance excludes pre-planned treatments under tourist visas. Strong recommendation: apply S2 visa for medical activities. Visa-free access works for 30-day simple treatments. L visa creates unnecessary complications for healthcare travelers.
Q: How long does the medical visa process take?
Complete timeline averages 2-3 weeks for standard processing. Hospital invitation letters require 3-7 business days. Document preparation consumes 2-3 days for gathering translations. Embassy processing adds 4-5 business days under standard. Expedited service reduces processing to 2-3 business days. Emergency cases with critical documentation may qualify 24-hour. Peak seasons add 3-5 days during holidays. Begin applications 4-6 weeks before treatment dates.
Q: What if my condition worsens and I need extended stay?
Apply for visa extension at local Public Security Bureau. S2 visa extends maximum twice, each up to 90 days. Provide hospital-issued continuation treatment certificate justifying extension. Extension applications require seven-day processing time minimum. Apply before visa expiry always to maintain legal status. Treatments exceeding 180 days should convert to residence permits. Extension fees cost ¥160 RMB per application approximately. Alternative: exit China and reapply new S2 visa.
Q: Is medical insurance mandatory for obtaining China medical visa?
Medical insurance not officially mandatory for S2 applications. Some embassies may request insurance proof depending on regulations. Hospital international departments typically require insurance or cash deposits. Insurance protects against unexpected complications and emergency evacuations. Minimum recommended coverage: $50,000 USD medical benefits. Include medical tourism activities in policy coverage specifically. Travel insurance premiums range $50-$200 based on coverage. Strongly recommended despite not being officially required.
Q: Can my family members accompany me using the same visa?
Family members must apply for individual S2 visas separately. No joint application category exists for china medical visas. Accompanying spouses, parents, or children apply under S2 "companion". Provide additional kinship proof like marriage or birth certificates. Other relatives should apply for L tourist visas. Utilize visa-free exemption if eligible nationality applies. Simultaneous applications typically processed together by embassy. Each person requires complete separate documentation package.
Q: Can I work remotely while in China on medical visa?
No, S2 visa strictly prohibits employment or profit-generating activities. Remote work for foreign employers exists in legal gray. Strongly discourage attempting remote work on medical visas. Discovered violations result in fines, deportation, and entry bans. Requiring long-term presence with work capability needs Z-visa. Medical visa purpose limited to treatment only strictly. Working remotely may constitute visa misuse under immigration law. Apply proper work visa instead of medical authorization.